(주)에스켐텍
Liquid Sodium Silicate
Chemical Composition : Na2O·nSiO2·xH2O
Synthesis method : Dry(indirect method) Wet(Direct Method)
Application : Silica gel, Solidification Silica, Industrial Lens, Casting, Adhesion Agent of Wood and Paper, Soap & Detergent Builder
Industrial Liquid Sodium Silicate : colorless transparent liquid or translucencem as a sirup
Industrial Solid Sodium Silicate : colorless, weak transparent liquid, translucence fine particle or solid of glass form
01 General Property
- If alkali decreases, It is seen property of silica gel or colloidal silica
- If water decrease, it is approach in anhydrous glass property
- If alkali increases, it is seen property of NaOH
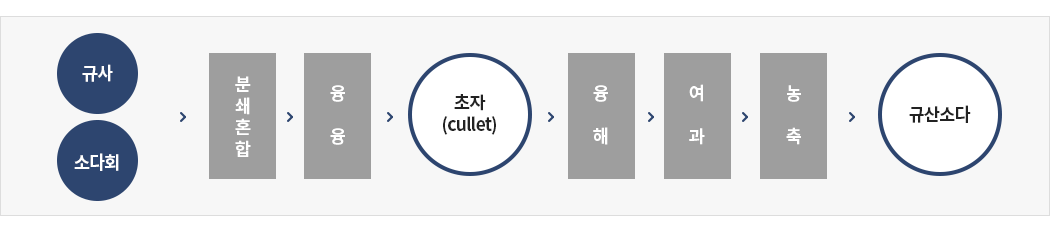
02 Synthesis Process
-
Indirect Method (Dry)
① Adjust combination rate of sodium carbonate and quartz sand, Pouring into melting furnace
② Cooling in the atmosphere (cullet)
③ Put it with water in reaction tank, heating and pressurization
④ Removing impurities by filtering
⑤ Concentration according to decided concentrate. Na2CO3 + nSiO2 → Na2O·nSiO2 + CO2
-
Direct method (Wet)
① Adjust combination rate of NaOH and quartz sand, Pouring into reaction tank directly
② Reaction with high pressure steam and filtering, concentration.
03 Physico-chemistry Properties
-
1. Composition
Liquid Sodium silicate Chemical composition : Na₂O·nSiO₂·xH₂O Hydrated polymeric silicic acid is forming O-Si-O bonding by combined OH and Na, but it has very weak bonding strength with Na, because perfectly hydrate reaction of bonding -
2. Specific Gravity
If temperature is increasing, specific gravity is decreasing Baume degree measures at 20℃ Be(20℃) = [(20-t) × 0.04]
Composition and physical properties of liquid sodium silicate (20℃)Na2O SiO2(%) Mole Ratio Baume Viscosity(CP) 19.7 31.2 1.6 58.0 3,000 14.7 29.4 2.1 50.0 122 13.9 33.4 2.4 52.0 640 10.6 26.9 2.6 42.0 23 11.2 31.9 2.9 47.0 250 10.3 30.9 3.1 44.6 150 9.1 29.2 3.3 41.5 75 8.8 29.1 3.4 41.0 110 6.6 25.3 4.0 34.0 75 -
3. Viscosity
At same mole ratio, if solid content is increase, viscosity is increase At same solid content, if mole ratio is decrease, viscosity is decrease Even if mole ration is decreased that specific gravity is increasing, viscosity is increasing If temperature is increasing, viscosity is decreasing At same viscosity, if mole ratio is decreasing, specific gravity is increasing -
4. pH
Buffer phenomenon at pH 11.5~13.0 If mole ratio is decreasing( content increase), pH is increasing -
5. Freezing point
Liquid sodium silicate has -2.5℃ freezing point at mole ratio 3.3, solid content 38% 32℃ freezing point at mole ration 2.0, solid content 54% Frozen liquid sodium silicate forms orthorhombic phase, but if it is melt by heating, get recover ...properties of original state again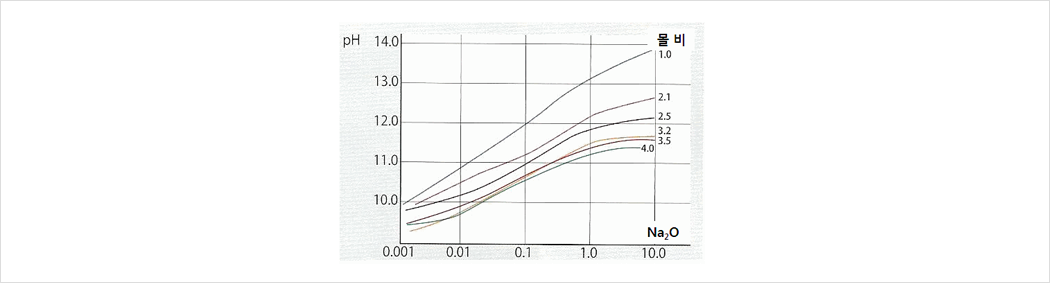
-
6. Freezing point If sodium silicate neutralize by acid, separates instantaneously and creates Gel.
Also, shrinkage appearance by release of water, losing the basic property of sodium silicate
7. It is possible more than 1,000℃ heating temperature that 100% dehydration of liquid sodium silicate. Also, basic property of sodium silicate does not change even if dehydration happens.
8. Al, Ca, Ba etc. ion reaction with matallic hydroxide sodium silicate and water, it is create precipitated material that has various color
9. Add alcohol in liquid sodium silicate, create gel by hydrate reaction
04 Treatment, caution
-
Sodium silicate is medicines of harmlessness that nontoxic chemical Only, If it is drink, harmful in human body, because is not food additive
- When contact in skin, must washing by water.
- When contact in eye, must put in eyewash after washing by water and boric acid solution
- Take care do not contacted in wound region.
- When Stick to stained cloth, If it do not washing instantly by warm water, decoloration occur in cloth
05 Application
| Application | Mole Ratio | Principle Property | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Binding | Origin of silicic acid | Chemical reaction | Disperse emulsification | Neutralization Soap making |
Peroxide stabilizer |
||
| Paper box | 3.3 | ○ | |||||
| Welding rod | 2.8~3.3 | ○ | |||||
| Paint | 3.3 | ○ | |||||
| Casting | 2~2.7 | ○ | ○ | ||||
| Soil strengthning | 3.3 | ○ | |||||
| Water treatment | 3.3 | ○ | |||||
| Anhydrous silicic acid | 3.3 | ○ | ○ | ||||
| Refractory | 3.3 | ○ | ○ | ||||
| Chemical product | 2~3.3 | ○ | ○ | ||||
| Cement | 2~3.3 | ○ | |||||
| Textile | 2~3.3 | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||
| Paper making | 2~3.3 | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||
| Detergent | 2~3.3 | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||

1. Casting Binder
It is use of gel formation of sodium silicate that used 2.1 - 3.2 mole ration. widely use of Silica Gel formation process that adds sodium silicate solution and CO2 to the iron-casting sand, because it has many advantage of low equipment and labor cost, less space, bed smell does not happen.
2. Soil strengthning
Main raw material of waterproof agent for construction industry. Sodium silicate solution applied to underground water treatment of high water content ground and soil improvement etc.

3. Detergent (Soap, Synthetic Detergent)
Act by trillion Builder of cleaning material and does softening action of hard water. Directly Harmonized with alkali in liquid sodium silicate and CO₂ that is dissolution acidic carbonate while it is making micro-precipitate of soft gel phase reaction with Calcium or Magnesium salt, and floating in solution. It is used as Buffer action and Suspension Emulsifying, achieve corrosion prevent operation of aluminum, zinc etc in detergent.
4. Ceramic Binder
Liquid sodium silicate that has 2.0-3.4 mole ratio makes soaks surface easily and permeation in limit occur and it has properties of matter of suitable viscosity, it is used in adhesion of paper box and asbestos paper tube product. Also recently, study has been lively that matched new inorganic adhesive by several kind of mixed organic, inorganic material
5. Paper making, Pulp
Liquid sodium silicates use for stabilizer of hydrogen peroxide in occasion of pulp, paper bleaching and black color removing agent
6. Cement
It is use of cement binder for acid, fire proof and adhesion of refractory.-
7. Silica Sol, Water Treatment
If sodium silicate neutralize by acid, polymerization occur by silicic acid released and silica sol formed that has negative charge by micro-particle. This silica sol is use of coagulate agent for natural water and waste water.
-
8. Chemical Product
Silica gel formed by acidification of sodium silicate, and also, micronized sodium silicate powder formed by acidification of sodium silicate that is called "white carbon" and it is widely use of rubber filler
-
9. Sodium silicate widely use of synthesis of metallic silicic acid, raw material of meta sodium silicate, and textile ceramic etc.
Korea industrial standard KSM 1415
Item No.1 No.2 No.3 No.4 Specific Gravity (20℃) 1.690 ↑ 1.590 ↑ 1.380 ↑ 1.260 ↑ Insolubility in water(%) 0.2 ↓ 0.2 ↓ 0.2 ↓ 0.2 ↓ Na2O (%) 17 - 18 14 - 15 9 - 10 6 - 7 SiO2 (%) 36 - 38 34 - 36 28 - 30 23 - 25 Fe2O3 (%) 0.05 ↓ 0.05 ↓ 0.03 ↓ 0.03 ↓
주소 : 경기도 안산시 단원구 해봉로 101
Tel : 031-492-4951 | Fax : 031-492-4954 | E-mail : sale@shsilicate.com
Copyright ⓒ (주)에스켐텍 All rights reserved.


